Mathematical Research
Sparse Optimization and Minimum Generator of Persistent Homology (Inverse Problem)
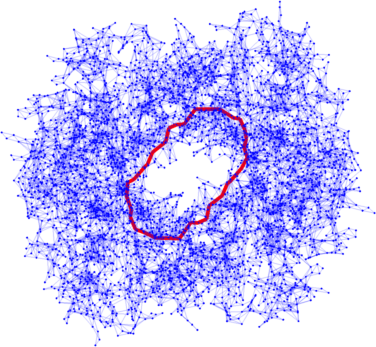
Persistent homology analyzes topological and geometric features of the data by reducing it into the so-called persistence diagrams. Then, it is significantly important to explicitly detect the subsets of the data which generate those topological and geometric features (e.g., material designs, and geometric analysis of atomic structures and functions of molecules). This problem can be formulated as an inverse problem using sparse linear optimization which solves an optimum generator (usually minimum generators w.r.t. the number of simplices) from a characteristic generator in persistence diagrams.
literatureE. Escolar and Y. Hiraoka. Optimal Cycles for Persistent Homology via Linear Programming. Optimization in the Real World --Towards Solving Real-World Optimization Problems--. Mathematics for Industry, Springer (2015).